LLMs 下的文本 OoD 检测
由于签证的原因,今年又不能去 ACL 了,还是分享我们在 ACL23 的一篇工作,顺便聊聊 LLMs 时代下 Text OoD Detection。(希望能够在 EMNLP23 or ACL24 见到大家)
Multi-Level Knowledge Distillation for Out-of-Distribution Detection in Text (ACL 2023)
✍️Qianhui Wu, Huiqiang Jiang, Haonan Yin, Börje F. Karlsson, Chin-Yew Lin.
👨💻 Code in Github (仍在合规审核中)
TL;DR: 本文提出了一种基于多层级知识蒸馏的非监督文本 OoD 检测方法,通过混合不同层级的知识,蒸馏至from-scratch的student model中,学习到不同level的语言、语义知识,从而提升 OoD 检测的性能。除了在OoD Detection 任务上的实验之外,我们还在AIGC生成文本检测任务(HC3)上进行测试,得到了近乎接近Supervised的结果。
In the era of LLMs
LLMs 具有极强的领域间泛化能力,对于 LLMs 而言,还存在 OoD 吗?这一方向还有研究价值吗?
首先,LLMs 肯定还存在 OoD,最直观的是低资源语言 OoD,例如非英语环境下的 LLaMA。 此外,在一些特定领域知识上,LLMs 也存在 OoD,但随着 RLHF 和更高质量的数据,这种情况在 GPT-4 中越来越少。
其次,如果不局限于原始的 OoD Detection 任务,将其拓展为一个更大的任务,即Detection using Out-of-Distribution,这个问题在 LLMs 中仍然存在,且是一个重要问题。举两个简单的例子:
- MLKD 中测试的 AIGC 文本检测任务,即检测文本是否来自 LLMs,可用于作弊、bot 等检测;
- 由于 AIGC 生成 token 的分布较为相似,而人类书写的分布更加多样,非监督地使用 LLMs 生成的 ID 文本构建 OoD 检测器,可以高效地识别 AIGC 生成文本。
- 缓解 LLMs 的 alignment tax, Yuntao Bai et al[1]. 提出 Alignment Tax 产生的一个原因是 LLMs 在 alignment 过程中有益性和无害性之间的 trade-off,而利用 OoD Detector 过滤有害性文本,可以缓解这种 trade-off,提升 LLMs 的性能。
此外,我们还有一些有趣的想法,不过还在 review 中,之后再和大家分享。
Motivation
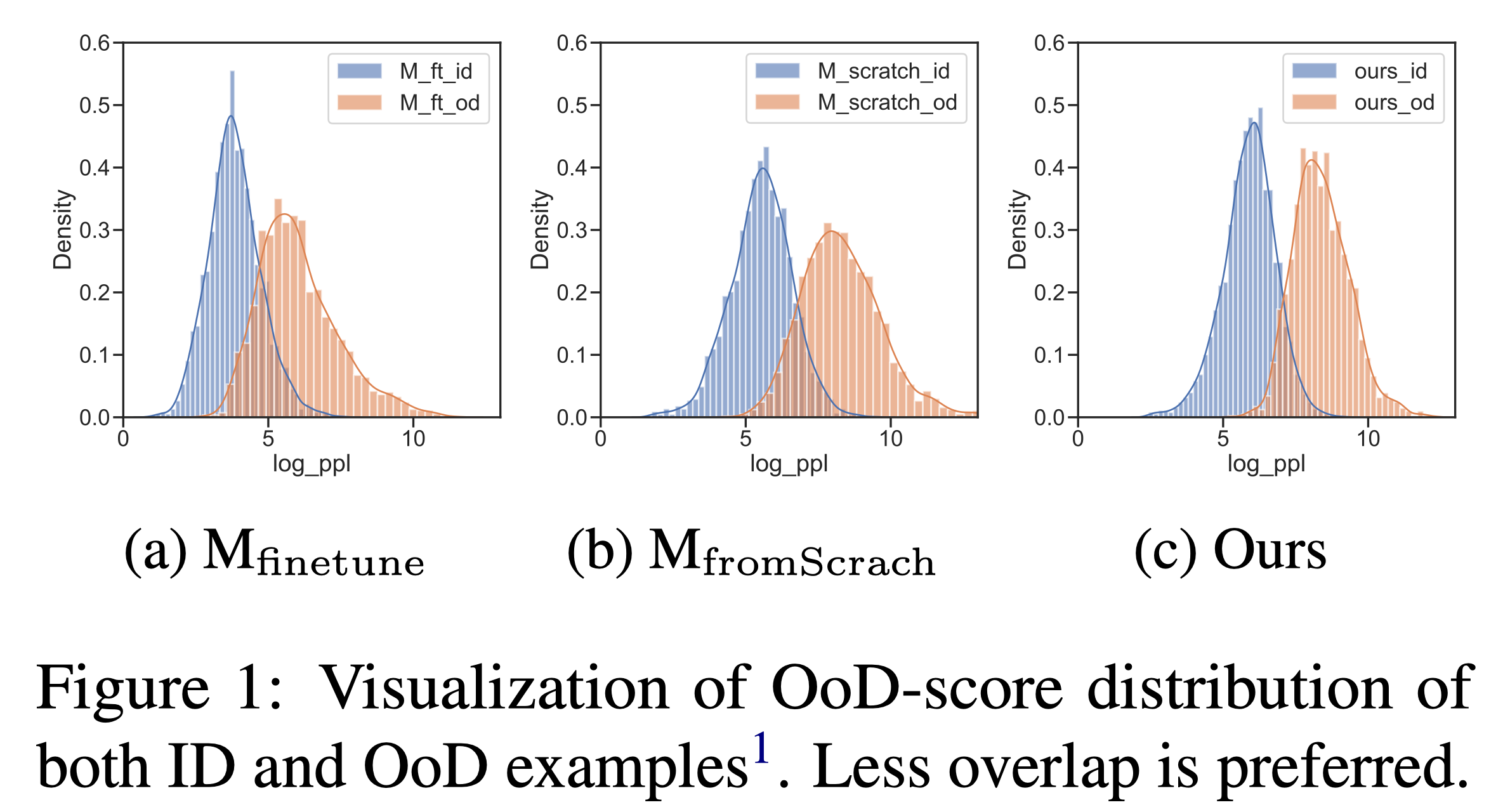
考虑在 w/o supervision from both OoD data nor ID class labels 的 OoD Detection 任务中, 预训练的 LM 由于见过非常多的 raw text,即使是在 ID 中 finetune 过得模型$M_{\text{finetune}}$,对于特定 ID 数据集之外的 OoD 已经具有和 ID 相近的 distrubution。 如果此时通过一个 model 只在 ID data 中 from scratch 的训练$M_{\text{fromScrath}}$,能够缓解上述问题。但是由于 from-scratch 训练语料较少,可能会导致 ID 数据的分布空间松散,从而造成 OoD data 有更多机会处于 ID 数据的分布中,见图 1。
MLKD
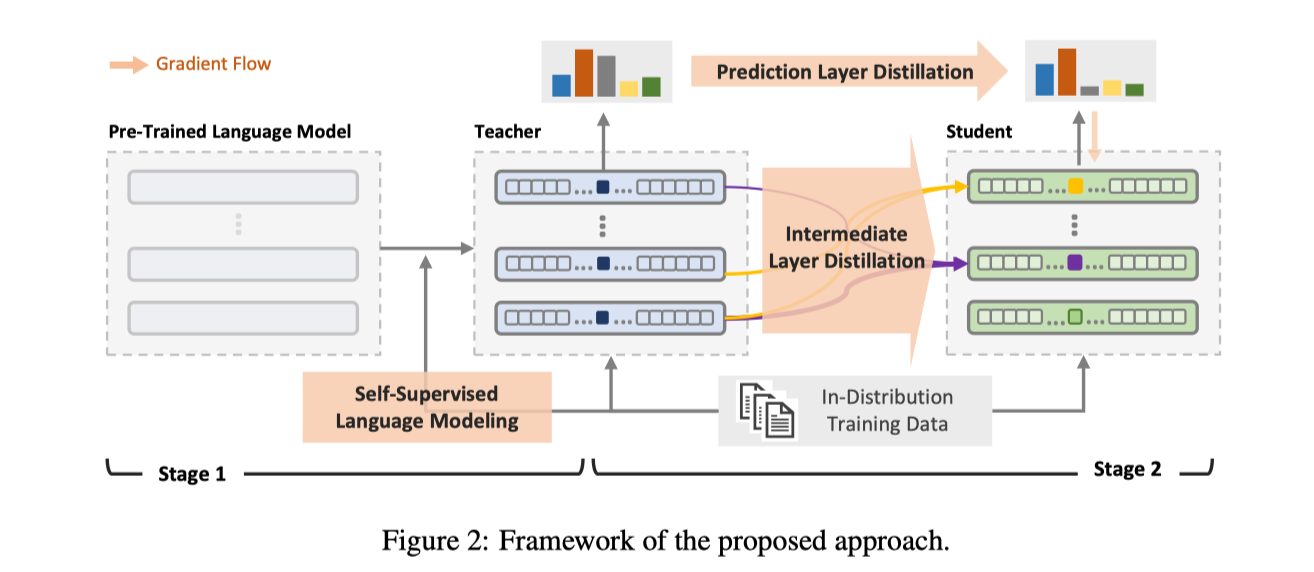
那么很自然的想法是利用一个在 ID 数据中 finetune 过得 model $M_{\text{finetune}}$作为 teacher model,from-scratch 的 ID 数据中蒸馏一个 student model, 见式$\ref{equ:loss-kd}$。
\begin{equation} L^{\textbf{x}}_{pred}(\theta_{stu}) = \quad -\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^N \mathrm{KL} \left(p(x_i|x_{<i}; \theta_{tea}), p(x_i|x_{<i}; \theta_{stu})\right), \label{equ:loss-kd} \end{equation}
考虑到之前的工作[2]发现,融合不同 layer 对应的语义信息能提升 OoD Detection 效果,本文也引入 Layer-wise KD,将不同层级的语义信息融合到 student model 中。
\begin{equation} s_{l,i}(j) = -\left\Vert h_{l,i}^{stu} - W_j h_{j,i}^{tea}\right\Vert_2, \label{equ:loss-s} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} {L}_{(l)}^{\textbf{x}} (\theta_{stu})=\frac{1}{N}\frac{1}{K} \sum_{i=1}^N \sum_{k=1}^K - \beta_{k} \cdot s_{l,i}^k(\cdot). \label{equ:loss-lkd} \end{equation}
综上所述,总的训练目标为,
\begin{equation} {L} (\theta_{stu}) = \sum_{\textbf{x}\in {D}_{in}} \left(\lambda {L}_{pred}^{\textbf{x}} + (1-\lambda)\sum_{l\in {T}} {L}_{(l)}^{\textbf{x}}\right), \label{equ:loss-total} \end{equation}
Experiments
在 CLINC150,SST, ROSTD, 20NewsGroups 和 AGNews 上对 OoD Detection 任务进行测试。
\begin{array}{l|ccc} \hline \textbf{Method} & AUROC (\uparrow) & AUPR (\uparrow)& FAR95 (\downarrow) \\ \hline TF-IDF+SVD^{\dagger} & 58.5 & 21.8 & - \\ MDF+IMLM^{\dagger} & 77.8 & 39.1 & - \\ MDF+IMLM & 77.46 \pm{0.33} & 39.23 \pm{0.52} & 65.87 \pm{1.13} \\ DATE & 83.38 \pm{0.15} & 50.21 \pm{0.18} & 66.67 \pm{1.65} \\ \hline M_{\mathrm{finetune}} & 89.76 \pm{0.13} & 62.39 \pm{0.29} & 33.77 \pm{0.91} \\ M_{\mathrm{fromScratch}} & 91.73 \pm{0.12} & 68.78 \pm{0.62} & 28.31 \pm{0.40} \\ Ours & {92.51 \pm{0.18}} & {70.94 \pm{0.78}} & {27.16 \pm{0.65}}\\ \hline \end{array}
上表展示了 CLINC150 数据集上的结果,其中$\dagger$表示原论文中的结果。
我们还对不同模块对最终结果的贡献做了相关的 ablation 实验。
\begin{array}{l|ccc} \hline & AUROC (\uparrow) & AUPR (\uparrow)& FAR95 (\downarrow) \\ \hline Ours & {97.97 \pm{0.40}} & {97.81 \pm{0.42}} & {9.50 \pm{2.09}} \\ Ours\ w/\ GPT2\_Init\_\theta_{stu} & 94.12 \pm{0.60} & 94.21 \pm{0.64} & 31.72 \pm{3.20} \\ Ours\ w/o\ {L}_{(l)}^{\textbf{x}} & 97.07 \pm{0.23} & 96.94 \pm{0.23} & 14.53 \pm{1.05} \\ \hline \end{array}
可以看到预训练的 distrubution 会干扰 ID/OoD 分布的判别,引入 layer-wise KD 能融合一部分不同层的语义信息,提升 OoD Detection 效果。
我们还对不同方法学到的 sentence represent 进行可视化,如下图所示。
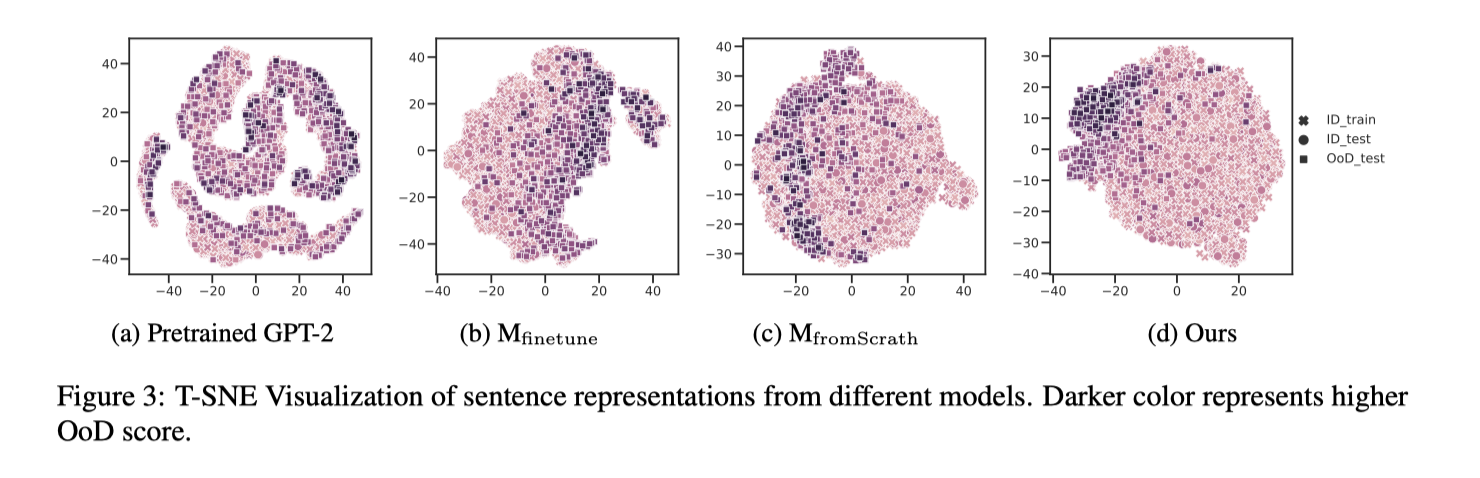
可以看到 pretrain 的 LM ID, OoD 完全重合在一起且十分分散;$M_{\text{finetune}}$虽然 OoD 相对聚集在一侧,但与 ID 的重合度较高;$M_{\text{fromScratch}}$ ID 与 OoD 拉的更开,但是由于 from scratch 语料的限制,导致一部分 OoD 也被分到 ID 的区域内;而$Ours$的分布图中 OoD 更为聚集,且与 ID 的重合度更低,说明$Ours$能更好的区分 ID 和 OoD。
除此之外,我们还在 HC3 数据集中,进行 AIGC 生成语料的 detection 实验,其中将 ChatGPT 生成的文本视为 ID dataset,human generated answers 视为 OoD test dataset,如下表所示。
\begin{array}{l|ccc} \hline & AUROC (\uparrow) & AUPR (\uparrow)& FAR95 (\downarrow) \\ \hline \textit{Unsupervised methods:}\\ DATE & 75.80 & 91.20 & 85.15 \\ MDF+IMLM (BERT) & 89.61 & 96.80 & 42.35 \\ MDF+IMLM (GPT2-small) & 91.53 & 92.56 & 31.84 \\ Ours & 99.80 & 99.95 & 0.61 \\ \hline \textit{Supervised method:} \\ chatgpt-detector-roberta & 99.98 & 99.99 & 0.04 \\ \hline \end{array}
感谢 HC3 的作者在 ACL23 投稿期间对我们的帮助。
总结
本文介绍了一种利用多层次知识蒸馏的非监督的 OoD Detection 方法,除了在传统 OoD Detection 数据上的结果之外,还在 AIGC 生成语料上进行了实验,取得了很好的效果。 除此之外,本文还探讨了 LLMs 时代中 OoD Detection 任务的意义与空间,希望能对相关研究有所启发。
[1] Training a Helpful and Harmless Assistant with Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback.
[2] Unsupervised Out-of-Domain Detection via Pre-trained Transformers.